| Share/Comment | |||
 |
Tweet |  |
|
 |
Feedback |  |
|
Six Sigma is usually related to the magic number of 3.4 defects per million opportunities. People often view Six Sigma as yet another rigorous statistical quality control mechanism.
Pioneered at Motorola in the mid-1980s, Six Sigma was initially targeted to quantify the defects occurred during manufacturing processes, and to reduce those defects to a very small level. Motorola claimed to have saved several million dollars. Another very popular success was at GE. Six Sigma contributed over US $ 300 million to GE's 1997 operating income.
Today Six Sigma is delivering business excellence, higher customer satisfaction, and superior profits by dramatically improving every process in an enterprise, whether financial, operational or production. Six Sigma has become a darling of a wide spectrum of industries, from health care to insurance to telecommunications to software.
What is 6 Sigma?
It is important to recall that every customer always values consistent and predicable services and/or products with near zero defects. Therefore they experience the variation and not the mean. Mean is their expectation, and our target.
If we can measure process variations that cause defects i.e. unacceptable deviation from the mean or target, we can work towards systematically managing the variation to eliminate defects.
Six Sigma is a methodology focused on creating breakthrough improvements by managing variation and reducing defects in processes across the enterprise.
Sigma is a Greek symbol represented by "σ".
Why is Six Sigma called Six Sigma, and not Four or Five Sigma or Eight Alpha (another Greek symbol)? Sigma is a statistical term that measures process deviation from the process mean or target. Mean is also referred to as average in common language. The figure of six was arrived statistically by looking at the current average maturity of most business enterprises. We would like to revise this figure to 8 or may be 9, provided the world becomes a more orderly and predictable (even with increasing entropy or chaos) place to live in!
There is a detailed discussion on keywords "breakthrough improvement" and "variation" apart from the "methodology" in later sections.
Example
Consider a pizza delivery shop that guarantees the order delivery within 30 minutes from the time of accepting an order. In the event of a delivery time miss, the customer is refunded 100% money. How often do we notice timely delivery from a thirty-minute pizza delivery shop? In contrast, we always take note of delayed deliveries, or that shop’s variation. This pizza shop will have to make 99.9997% deliveries within 30 mins to be called a six sigma shop.
It is evident that the "delivery time" is a critical-to-quality parameter from the customer perspective and has a significant impact on profits. In addition, it is an entry barrier for the competition. Such a parameter is called a CTQ and its definition in context of our pizza shop is given below:
CTQ Name: Timely Pizza delivery
CTQ Measure: Time in Minutes
CTQ Specification: Delivery within 30 minutes from the order acceptance time
Now we can easily define a defect:
Defect: Delivery that takes longer than 30 minutes
Unit: Order
Opportunity: 1 per order i.e. only "1" defect can occur in "1" order
The Six Sigma conversion graph illustrating the relationship between sigma values and defects/million opportunities is given below:
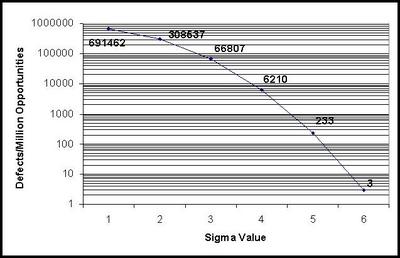
This graph is on a logarithmic scale. Notice the increasing rate of improvement. For example, 1 sigma to 3 sigma is only 10 times improvement; 3 sigma to 4 sigma is a big 10 times improvement; whereas 5 sigma to 6 sigma is a whooping 1825 times change. That is why it is essential to achieve breakthrough improvements to reach such a level of maturity. Six Sigma provides a methodology to achieve this.
How does 6 Sigma work?
The driving force behind any Six Sigma project comes from its primary focus - "bringing breakthrough improvements in a systematic manner by managing variation and reducing defects". This requires us to ask tougher questions, raise the bar significantly, and force people to think out of the box and to be innovative. The objective is to stretch, and stretch mentally not physically. To make this journey successful there is a methodology(s) to support Six Sigma implementations.
There are two potential scenarios - First, there is already an existing process(s) that is working "reasonably" well; and second there is no process at all. A bad process is as good as no process.
The first scenario focuses on significant process improvements and requires use of DMAIC:
- Define process goals in terms of key critical parameters (i.e. critical to quality or critical to production) on the basis of customer requirements or Voice Of Customer (VOC)
- Measure the current process performance in context of goals
- Analyze the current scenario in terms of causes of variations and defects
- Improve the process by systematically reducing variation and eliminating defects
- Control future performance of the process
The second focuses on process design using Design For Six Sigma (DFSS) approach. DFSS typically requires IDOV:
- Identify process goals in terms of critical parameters, industry & competitor benchmarks, VOC
- Design involves enumeration of potential solutions and selection of the best
- Optimize performance by using advanced statistical modeling and simulation techniques and design refinements
- Validate that design works in accordance to the process goals
Note, sometimes a DMAIC project may turn into a DFSS project because the process in question requires complete re-design to bring about the desired degree of improvement. Such a discovery usually occurs during improvement phase of DMAIC.
It is extremely important to remember that Six Sigma is not just about product quality where only three products in a million are defective. It is about what is important or critical to the customer, whether internal or external. It is focuses on value in context of the customer and the market. For example, Polaroid had a sale of over US$ 2 billion in 1988 and was doing very well on stock exchange. It embraced Six Sigma and became a Six Sigma company some time around 1997. In late 2001, they filed for bankruptcy. This is because Polaroid only focused on improving the quality of their products and failed to assess the needs of their customers.
| Share/Comment | |||
 |
Tweet |  |
|
 |
Feedback |  |
|
Today Six Sigma focus has moved from simple "defect reduction" to "cost reduction" to "value creation", as pointed out by Mikel Harry. The objective is not to achieve the magic number of 3.4 DMPO but to beat your nearest competition by just 0.5 sigma in overall business excellence. Recall that 1 sigma improvement can mean over 1800X improvement - a huge barrier for competition to overcome.
comments powered by Disqus
Commenting Guidelines
We hope the conversations that take place on “discover6sigma.org” will be constructive in context of the topic. To ensure the quality of the discussion stays in check, our moderators will review all the comments and may edit them for clarity and relevance.
The comments that are posted using fowl language, promotional phrases and are not relevant in the said context, may be deleted as per moderators discretion.
By posting a comment here, you agree to give “discover6sigma.org” the rights to use the contents of your comments anywhere.