| Share/Comment | |||
 |
Tweet |  |
|
 |
Feedback |  |
|
A pool of ideas, generated from a brainstorming session, needs to be analyzed, prioritized before they can be implemented. A smaller set of ideas are easy to sift through and evaluate without applying any formal technique. Affinity diagramming is an effective technique to handle a large number of ideas. It is typically used when
- Large data set is to be traversed, like ideas generated from brainstorming and sieve for prioritization.
- Complexity due to diverse views and opinions.
- Group involvement and consensus.
Association, kinship, likeness are synonymous to affinity, and they are the underlying principle to be followed while adopting this technique. The process of affinity diagramming requires the team to categorize the ideas based on their subject knowledge thereby making it easy to sift and prioritize ideas.
Prerequisites for an Affinity Session
- An idea set generated from a Brainstorming Session, typically captured in form of Post-it Notes.
- Team should include people who have the necessary knowledge and skills to meld opinions, perspectives and are aware about the problem at hand. Too small or a very large team may not be effective. Rule of thumb suggests between 4 to 6 members in the team.
- Invitation that clearly states the purpose of the session.
- A facilitator is required to conduct the session.
How to conduct an Affinity Session
- Select and block a (Lively) room free from interruptions and distractions.
- Initiate the session by explaining the purpose, possibly already written and highlighted on the board.
- Place the Post-its randomly on the board/flat surface, ensuring visibility to all.
- Set the first objective as sorting ideas, opinions & issues based on the most natural relationship amongst them.
- Invite participants to get involved in the exercise of creating like groups from the idea pool.
- Participants should look for ideas that are related in some way, move the post-its for the like ideas to be together. The process should be followed till all ideas have been grouped.
- Resolve conflict of ideas falling in more than one group by placing another post-it with the same idea in both groups.
- Participants now can discuss on the patterns identified and focus on the controversial ideas. A consensus can be reached by discussion, making the changes in grouping.
- When ideas are grouped, select the heading to categorize each group. A meaning full but short heading represents the key thought of the group being assigned to. Now move groups under their respective headings to view the Affinity Diagram.
At the end of session, team is ready with Affinity Diagram, the categorized ideas are now ready for further shortlisting, if required.
Affinity Diagram Example
Following diagrams show a simplified sample for our famous timely pizza delivery problem.
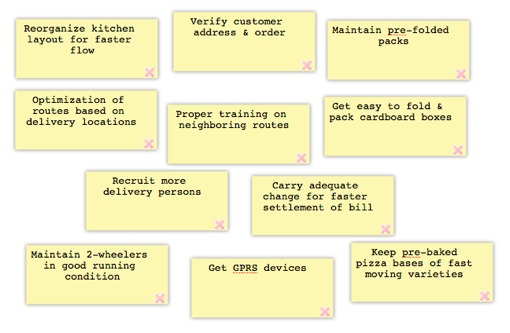

In real life, brainstorming & affinity diagramming techniques also find their applications while using other quality management tools and techniques. For example, while creating FMEA, possible cause of failures can be discovered through a brainstorming session and subsequently they can be categorized into different risk categories using affinity diagramming.
comments powered by Disqus
Commenting Guidelines
We hope the conversations that take place on “discover6sigma.org” will be constructive in context of the topic. To ensure the quality of the discussion stays in check, our moderators will review all the comments and may edit them for clarity and relevance.
The comments that are posted using fowl language, promotional phrases and are not relevant in the said context, may be deleted as per moderators discretion.
By posting a comment here, you agree to give “discover6sigma.org” the rights to use the contents of your comments anywhere.